Exporting Power: Türkiye’s Defence Industry and the Politics of Strategic Autonomy
 By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
Over the last decade, the development of Turkey’s defence industry has become a crucial aspect of its soft power diplomacy in both regional and global politics. The country has made significant efforts to invest heavily in the development of its indigenous defence industry, reducing its dependence on imports and becoming a leading defence exporter in global markets. The rapidly changing regional and global geopolitical landscape, particularly after the Arab uprisings, has prompted Ankara to expand the country’s defence industry and reduce its reliance on overseas arms procurement and international supply chains. Since the ruling AKP government came to power, the country’s indigenous defence industry has undergone a significant transformation, steadily becoming the twelfth-largest arms exporter, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). Given the regional instability marked by violent uprisings and sectarian conflicts, Türkiye’s pursuit of defence industry development can be understood as a primarily threat-driven strategy. This approach reflects an effort to enhance national defence capabilities and ensure strategic autonomy in response to both external security challenges and internal vulnerabilities. READ MORE
- December 22, 2025 08:29AM
How China Shapes the Drone Divide in the Russia-Ukraine War
 By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
The war in Ukraine has evolved into a complex geopolitical conflict while demonstrating the transformative role that drone technology has played in shaping the course of the war. Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, the Ukrainian Armed Forces began to actively embrace modern warfare technology, especially the use of First-Person Drones (FPVs) which were critical in inflicting grave damage on Russian forces using ‘meat grinder’ tactics to storm Ukrainian front-line positions. In the past two years, Ukrainian forces have used FPV drones for real-time intelligence and reconnaissance of Russian positions and troop movements while also deploying cost-effective “kamikaze” drones to target Russian recruits, tanks, howitzers, and other armoured vehicles. Although drone technology is now a core part of Ukraine’s struggle against Russian intervention, Kyiv initially faced an acute shortage of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in the early stages of the war, while the requirements of its frontline forces were partially met by civilian drones, mostly produced by the Chinese company DJI. READ MORE
- December 22, 2025 07:00AM
Iran–Israel War’s Implications for Armenia
 By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Senior Research Fellow at the APRI Armenia
By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Senior Research Fellow at the APRI Armenia
The June 2025 12-day Iran–Israel War and US military strikes targeting Iranian nuclear sites created shock waves in the Middle East and beyond. Iran and Israel exchanged strikes twice in 2024, but these were limited and mostly symbolic operations. While the war did not solve critical issues between Iran and Israel, and there is a possibility of another escalation, it demonstrated the volatile nature of Middle Eastern geopolitics, shaped by evolving balance of power. Armenia is a neighbour of Iran, and this fact alone is enough to mean that Armenia will be affected by any Iran–Israel confrontation. However, there are other factors that can amplify the implications for Armenia of a potential long-term war against Iran.
READ MORE
Conflict in the South Caucasus and the Middle East  By Alan WHITEHORN, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada By Alan WHITEHORN, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada
Armenia and the South Caucasus were historically parts of the former Soviet Union, and are often considered, in geopolitical terms, to be in the so-called Moscow-influenced “Russia’s near abroad”. It might be useful, however, to recognize the significant connections of the South Caucasus to the Middle East. In fact, Armenia is relatively close geographically (under 1,000 km) to each of the capital cities of Teheran (Iran), Baghdad (Iraq), and Ankara (Turkiye) and not much farther from Israel and Lebanon (under 1,300 km). In terms of international affairs and recent conflict Turkey has been a crucial military ally of Azerbaijan during the latter’s wars with Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh (Artsakh) in 2020 and 2023. A lesser-known fact is that, over the previous decade, Israel has been a major weapons’ supplier of Azerbaijan, particularly advanced drones that proved critical for Baku’s swift and decisive victory in the 2020 Armenia-Azerbaijan war, and its 2023 recapture of Nagorno-Karabakh, which displaced over 100,000 civilians, virtually all of the local Armenian population. READ MORE
A New and Technological Approach to Elections Begins  The Central Election Commission held a meeting and a series of events today, July 26th. The primary agenda item was the preparation and high-level accomplishment of the upcoming elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies in full compliance with the Constitution and laws. The Central Election Commission held a meeting and a series of events today, July 26th. The primary agenda item was the preparation and high-level accomplishment of the upcoming elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies in full compliance with the Constitution and laws.
According to Article 128 of the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan, elections for the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies are scheduled to take place on the first Sunday of the third ten-day period of October in the year their term expires. Considering that the term of the deputies of the Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis and the Councils of People's Deputies ends in 2024, the elections will be held on October 27th of this year, and the election campaign will begin on July 26th, as decided by the Central Election Commission. READ MORE
The intersection between Turkey’s defence industry and its foreign policy  By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly” By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly”
After the end of the Cold War, Turkish decision-makers adopted a “top-down” strategy that capitalized on the dramatic shift in international arms production. Turkey aimed to look eastward to cooperate with China and Russia as its threat perception changed. In the second half of the 1990s, Turkey became a prominent Israeli arms purchaser. There were numerous factors behind this. First, Israeli weapons were a high-tech and credible alternative to NATO weapons. Second, unlike Europe and the U.S., Israeli arms purchases were not conditioned to Turkey’s domestic developments (democratization, human rights, minority rights…). Third, Israel and Turkey’s foreign policies overlapped in critical areas in the Middle East, aiming to contain Syrian and Iranian interests. Finally, deep relations with Israel were expected to be rewarded by pro-Israeli lobbying groups in the U.S. to counter the Armenian and Greek lobbies.
READ MORE
The likeliest scenarios for tomorrow’s Russia  By Marat Terterov, PhD, Founder, and former Executive Director of the EGF By Marat Terterov, PhD, Founder, and former Executive Director of the EGF
The folly of predicting Russia’s future
When undertaking the task of seeking to forecast a ‘likely scenario’ for tomorrow’s Russia, one has to start with a caveat – predicting Russia’s future and what fate awaits the country in light of its continued military excursion in Ukraine is like trying to find a needle in a haystack. In other words, it is almost impossible to predict future political developments in Russia with any real certainty. This includes any efforts to predict whether Russia will continue to remain the arch belligerent in Ukraine, or whether it will be prepared to make concessions, or to forecast what impact either (or other) of these developments in the current conflict in Ukraine will have on the Russian regime of Vladimir Putin.
READ MORE
What Does a Recent ISIS-K Terror Attack Mean for Turkey?
 By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
On January 28, 2024, masked assailants attacked a Roman Catholic church in Istanbul, killing one person. Shortly afterward, the Islamic State, through its official Amaq News Agency, claimed responsibility. Turkish police detained 47 people, most Central Asian nationals. The incident shed light on the growing presence in Turkey of a Central Asian offshoot of the Islamic State group known as ISIS-K for Khorasan, once a large portion of the Persian Empire now divided among Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asian states. The January 28 assault was the group’s first successful attack in Turkey since January 1, 2017, when jihadists invaded an Istanbul nightclub, killing 39 people and wounding nearly 80.
Since then, Turkish security forces have launched mass counter-operations against ISIS suspects in Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. The operations appear to have deterred deadly terrorist attacks in large urban and border areas and to have depleted the militants’ financial resources. With the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan in 2021, ISIS-K suspended overseas activities to focus more on Afghanistan and try to undermine the Taliban, which resumed control over the country after the Americans left. READ MORE
Is Azerbaijan Interested in Peace?  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
After the military takeover of Nagorno-Karabakh by Azerbaijan in September 2023 and the forced displacement of the Armenians who lived there, there were hopes in Armenia and abroad that an Armenia-Azerbaijan peace agreement was within reach. These hopes were based on the assumption that Azerbaijan had achieved its primary objective for the past 30 years: the full absorption of Nagorno-Karabakh into Azerbaijan without any Armenian claims over the region.
Since September 2023, Azerbaijan has controlled all of Nagorno-Karabakh, with only a handful of Armenians remaining there. The Armenian government has accepted this reality and has no intention of challenging it. Meanwhile, Azerbaijan has faced no repercussions from the US, the EU, or Russia for imposing a blockade on Nagorno-Karabakh in December 2022, ignoring the orders of the International Court of Justice, launching a military attack in September 2023, or forcing all Armenians to leave the region. It seemed that the time for peace had thus arrived – a peace that would formalize Azerbaijani control over Nagorno-Karabakh, settle relations with Armenia, and open the way for the normalization of relations between Armenia and Turkey.
READ MORE
Will an Armenia-Azerbaijan peace agreement be indefinitely delayed?  By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku
2023 ended with positive notes for the Armenia-Azerbaijan peace process, but the new year has so far failed to maintain the momentum. Despite a successful prisoner exchange, and Armenia’s endorsement of Azerbaijan’s COP29 candidacy, recent statements from the respective governments have presented a mixed picture. While the Azerbaijani side has not indicated any setbacks in the ongoing talks yet, the Armenian government has criticized the recent statements by the Azerbaijani leader as unconstructive for the peace process.
Complicating matters further, disagreements have intensified regarding the possible regulations along the Zangezur corridor. The latest developments highlight a disparity in the visions of Russia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan for this corridor. Unfortunately, these developments suggest that the obstacles in the Armenia-Azerbaijan peace treaty talks may be more fundamental, potentially leading to indefinite delays in the process.
READ MORE
- February 24, 2024 10:13AM
The UN General Assembly unanimously adopted a resolution initiated by Uzbekistan on environmental challenges in Central Asia  Qodir Djuraev, MP, Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis of the Republic of Uzbekistan Qodir Djuraev, MP, Legislative Chamber of the Oliy Majlis of the Republic of Uzbekistan
The UN General Assembly unanimously adopted the resolution on "Central Asia in the face of environmental challenges: strengthening regional solidarity for the sake of sustainable development and prosperity".
The resolution initiated and proposed by Uzbekistan and unanimously adopted by the UN General Assembly highlights the pressing environmental challenges faced in Central Asia. This region, known for its diverse ecosystems and natural resources, has been grappling with various environmental issues that require immediate attention and joint collaborative efforts. The resolution serves as a significant step towards addressing these challenges and fostering sustainable development in the region.
READ MORE
Armenia and Azerbaijan Address Concerns Over Territorial Integrity  By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku
On January 19, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan called for a new constitution in a meeting with senior officials from the Armenian Ministry of Justice. Pashinyan asserted that Armenia needs “a new constitution, not constitutional changes,” adding that the new foundational document would make the country “more competitive and viable in the new geopolitical and regional environment” (Azatutyun.am, January 19). He highlighted that the new constitution would maintain the present parliamentary system and underscored “external security” and “internationally recognized sovereign territory” as the main issues to be addressed. Mutual respect for one another’s territorial integrity remains a sticking point in peace negotiations between Armenia and Azerbaijan. If Yerevan proceeds with Pashinyan’s proposal, the new constitution will eliminate certain hurdles to signing a peace treaty with Baku.
READ MORE
Baku wants an agreement with Armenia without mediators  By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku
On January 8, US Senior Adviser on Caucasus Negotiations Louis Bono visited Yerevan, engaging in discussions with local officials regarding the Armenia-Azerbaijan peace process. The Armenian side reported that one of the issues discussed during this visit was the organization of a meeting of the Armenian and Azerbaijani foreign ministers in Washington. Unlike his previous visits to the region, this trip omitted a visit to Baku, suggesting that it either wasn’t planned, which is unlikely, or that the Azerbaijani side was not open to receiving him. Recent developments between Baku and Yerevan, along with the evolving dynamics of mediator involvement, indicate that Azerbaijan has grown more cautious and sceptical about the role of third parties in the Armenia-Azerbaijan process. As a result, Azerbaijan has advocated for bilateral meetings between the two countries. Baku’s position is primarily related with the potential geopolitical fallout of the upcoming peace deal with Yerevan.
READ MORE
What Next in Armenia – Azerbaijan Negotiations  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
In the late months of 2022 and 2023 there were intensive discussions about the possible signature of the Armenia – Azerbaijan peace agreement. Both international mediators and facilitators, as well as representatives of Armenia and Azerbaijan were making statements that a peace agreement signature is within reach. As we enter 2024, discussions are underway about the potential signature of the Armenia – Azerbaijan agreement in 2024. The December 7, 2023, bilateral statement on the release of Prisoners of War and Armenia’s support of the Azerbaijani bid to host the COP29 in Baku gave more impetus to these hopes. Some believe that the military takeover of Nagorno Karabakh by Azerbaijan in September 2023 made this perspective more realistic, especially as the Armenian government agreed not to include anything on Nagorno Karabakh in the peace agreement.
READ MORE
The Geopolitical Background of the Moscow-Yerevan Rift and Russia’s Future in the Region  By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly” By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly”
Recent geopolitical developments in the South Caucasus have once again appeared in the headlines of media and analytical centers. Experts have been questioning whether Russia is distancing itself from the region. Armenian regional experts and officials have been questioning Russia’s motives in the region, considering developments in Artsakh and the latest Azerbaijani escalation. Russia is navigating the narrow complexities of the post-2020 Artsakh War regional architecture, asserting itself as the main power broker in the region (i.e. brokering the 2020 trilateral ceasefire agreement, arranging humanitarian aid to Artsakh via the Berdzor Corridor and Aghdam, and possibly a new deal in the coming days) through compromise or political flexibility. This flexibility has caused friction in Moscow-Yerevan relations.
Many in Russia, including high officials, are suspicious of Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan’s motives towards their country. The Armenian leader has speculated that Russia seems to be leaving the region. However, Russia still views the region as “blizhnee zarubezhe” (its “near abroad”) or its “lebensraum” (its “vital space”). From Russia’s perspective, if it leaves the South Caucasus, its only route to the Middle East would be cut off, Iran and Turkey would clash for power, and the North Caucasus would become vulnerable to instability.
READ MORE
Azerbaijan Moves to Disarm Karabakh Separatists (Part Two)  By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku
On September 20, Azerbaijan called for a ceasefire in the operation against armed detachments of the separatist regime in Karabakh. In a televised address to the nation, President Ilham Aliyev stated that Baku’s conditions were accepted by the separatist entity. He announced that the “representatives of the Armenian community living in Karabakh, who refused to meet our representatives several months ago, are ready to meet in the city of Yevlakh. Azerbaijan has disclosed that 192 servicemen were killed and more than 500 wounded during the 24-hour “anti-terrorist operation”. The Armenian side has reported at least 200 people killed and more than 400 wounded.
In preventing further escalation, the Armenian government chose not to militarily intervene in the clashes on September 19 and 20. Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan characterized possible involvement as a threat to his country. He stated, “Armenia is not involved in military operations. I want to mention once again that Armenia does not have an army in Nagorno-Karabakh”.
READ MORE
Azerbaijan Moves to Disarm Karabakh Separatists (Part One)  By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku By Vasif HUSEYNOV, PhD, Head of Department, AIR Center, Adjunct Lecturer, ADA and Khazar Universities, Baku
On September 19, the Azerbaijani Defence Ministry announced it had launched an “anti-terrorist” operation against “illegal formations” in Karabakh. This move came after four Azerbaijani soldiers and two civilians were killed by land mines in the region. Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan condemned the “full-scale aggression” and denounced Russian peacekeepers for “failing to do their jobs’.
The recent fighting comes as tensions had been mounting over Baku’s efforts to fully integrate Karabakh back into Azerbaijan. This measure had been stipulated in the tripartite agreement signed by Azerbaijan, Armenia and Russia following the end of the Second Karabakh War in November 2020. Russian peacekeepers were stationed in the region to facilitate implementation of the measure; yet, they have done little since to constructively manage the process.
READ MORE
Avoiding another War in Karabakh  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
It seems that talks over the future of Nagorno Karabakh have reached an impasse. Azerbaijan claims there will be no Nagorno Karabakh inside Azerbaijan, and Armenians should live as ordinary Azerbaijani citizens. At the same time, those who do not want to accept this option should leave. Armenians of Nagorno Karabakh categorically reject this option, meanwhile stating that they will not leave their homeland. […] Currently, it is challenging to offer an option that may more or less satisfy both Azerbaijan and NKR. However, one thing is clear: new large-scale war in Nagorno Karabakh will make long-term peace and stability in the South Caucasus a pipe dream. Thus, all actors interested in a stable region should message Azerbaijan that a new war against Nagorno Karabakh is not the best option to move forward. Otherwise, the region will plunge into another decade of instability, destruction, and human suffering.
READ MORE
- September 25, 2023 22:43PM
Pushing Armenia to make further concessions will spoil any chance for peace  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
After a break of several months Armenia and Azerbaijan have now resumed their engagement in peace negotiations in earnest. After a face-to-face meeting between leaders in Munich in February, the Armenian and Azerbaijani ministers of foreign affairs went to Washington in early May 2023 to take part in the most intensive round of negotiations ever held since the Spring 2001 Key West summit between Presidents Heydar Aliyev and Robert Kocharyan. The ministers achieved progress, opening the path for the 14 May Brussels summit involving Prime Minister Pashinyan, President Aliyev, and President of the European Union Council Charles Michel. On 19 May, the Armenian and Azerbaijani foreign ministers met in Moscow, and a trilateral Aliyev - Pashinyan - Putin summit was scheduled for 25 May.
READ MORE
Diversification of Armenian Security and Defence Policy and the Role of India  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
The 2020 Nagorno Karabakh war has significantly changed the balance of power in the South Caucasus, increasing the role and influence of Turkey. The direct involvement of Turkey in the war and the lack of action by Russia to prevent this NATO member state from challenging the Russian zone of influence in the post-Soviet space crushed the basics of the Armenian foreign and security policy. Since the end of the first Nagorno Karabakh war in 1994, Armenian military doctrine has been based on the core belief that Russia will not allow direct Turkish involvement in a new war against Armenia. Thus, Armenia prepared itself for the war with Azerbaijan while outsourcing to Russia the deterrence of Turkey. Meanwhile, this mindset also resulted in a Russia-focused defence and security policy. Armenia was buying weapons mainly from Russia, almost all Armenian officers were studying in Russian military universities, and the structure and operating mode of the Armenian army was solely based on the Russian model. Armenia developed limited defence cooperation with other nations, including the US, Greece, and Poland, and signed its first Individual Partnership Action Plan with NATO in 2005. However, these sporadic interactions did not change the basics of Russia-focused foreign and military policy. READ MORE
A Long-Term International Presence in Nagorno-Karabakh Is Needed  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
Nagorno Karabakh's future is the most challenging question that Armenia and Azerbaijan face as they seek to move towards the normalisation of relations between them.
Since the 2020 Nagorno Karabakh war ended, Armenia and Azerbaijan have launched multi-track negotiations to sign a peace treaty. In 2021 the primary platform for negotiations was Russia, and in 2022 the EU and the US joined the club. Armenia and Azerbaijan discuss several separate but intertwined issues – the signature of the peace treaty, delimitation and demarcation of borders, restoration of communications, and the future of Nagorno Karabakh. All issues are pretty complicated, but Nagorno Karabakh's future is the most challenging question. There are different approaches how to deal with this issue. One approach argues for the inclusion of Nagorno Karabakh in the bilateral peace treaty, while according to another view, the Nagorno Karabakh issue should be separated from discussions on Armenia - Azerbaijan relations. READ MORE
After the De-occupation of Kherson: Winter Break or Attack on Crimea?  By Nika CHITADZE, PhD, Director of the Center for International Studies, Tbilisi By Nika CHITADZE, PhD, Director of the Center for International Studies, Tbilisi
As it is known, the liberation of Kherson has already been assessed as a great military and an important political and psychological victory for Ukraine. Now it is possible to analyze what new opportunities this gives to the Ukrainian army and how things will develop. At the same time, the Russian forces launched a massive offensive in the Donetsk region, and are carrying out more intensive missile attacks against the critical infrastructure of Ukraine, as a result of which, first of all, the civilian population of the country is harmed and the victims are increasing more and more. With all of the above, the Russians want to somehow cover up the Kherson disaster. At the same time, it is worth noting the fact that the Russian army is insufficiently equipped and not ready for the winter war. This is the main reason why the Russians are asking for negotiations. According to them, depending on the situation on the front, the events may develop in two scenarios - the parties take the so-called winter break, or the armed forces of Ukraine develop an offensive to the south - first in the direction of Melitopol and Mariupol, and then in the direction of Crimea.
READ MORE
- February 16, 2023 11:38AM
Post-Soviet Peace: We Demand Peace  An open letter signed by people from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkey, and other countries An open letter signed by people from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia, Turkey, and other countries
We, a group of people who stand for peace, from the post-Soviet space and its neighbourhood exhausted by never-ending wars and growing imperialist rivalry on our territories, are full of rage as we have observed Azerbaijan’s recent large-scale attack on Armenia. This, coupled with Russian Federation’s attack on Ukraine and the renewed military clashes in border areas between Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, raises heavy concerns regarding possible future escalations not only in the Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict but all other conflicts in the post-Soviet space.
The recent attack on Armenia has costed hundreds of lives within two days from both sides of the conflict, caused serious destruction to civil infrastructure in Armenia, displaced thousands, and further widened the gap between the countries and their people. We raise our persistent voices against the continuing warfare. READ MORE
No Peace Should not Mean War  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
The developments of the last three weeks have proved that Armenia and Azerbaijan are far from signing a peace agreement, at least by the end of 2022. There is a danger that Azerbaijan may interpret this as a failure of the peace process and use this as a "moral justification" to launch a new large-scale aggression. If this happens, it will push Armenia and Azerbaijan further back from any chance to reach an agreement and deepen the mutual mistrust.
In recent months Armenia – Azerbaijan negotiation process passed through several ups and downs. The September 13-14, 2022, Azerbaijani aggression seemed to jeopardize the fragile achievements reached during the three Brussel summits held in April, May, and August 2022. However, immediately after the ceasefire reached on September 14, there was a new push toward reaching a peace agreement. Armenian and Azerbaijani foreign ministers met in New York in late September and Geneva on October 2; Secretary of the Armenian Security Council Armen Grigoryan had a meeting with President Aliyev’s top foreign policy aide Hikmet Hajiyev in Washington on September 27, 2022. READ MORE
- December 13, 2022 05:37AM
New US National Security Strategy and Implications for Armenia  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
On October 12, 2022, the White House published President Biden’s first national security strategy. The document outlines the US’ primary goals for domestic and foreign policy and its future vision for the world. US national security strategies have been published every four years since the early 2000s, laying out the incumbent administration’s policy goals and strategic priorities. The 2002 and 2006 national security strategies were focused on the war on terror and democracy promotion. The Obama administration, while emphasizing democracy promotion, started to refocus the US’ attention on the Asia-Pacific region. Meanwhile, due to the 2014 Ukraine crisis, the February 2015 national security strategy included harsh rhetoric toward Russia. In December 2017, President Donald Trump focused his national security strategy on great power competition and US rivalry with China READ MORE
Scenarios for the Future of Nagorno Karabakh  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
In late May 2022, Armenia and Azerbaijan established national commissions for border delimitation and demarcation. The two countries are close to signing a deal on the restoration of communications and will soon launch negotiations on elaborating a bilateral agreement. Currently, experts and societies wonder what these developments mean for the future of the self-proclaimed Nagorno Karabakh Republic. Discussions are underway, and different ideas have been put forward. Some Azerbaijani experts started to circulate the possibility of autonomy for Nagorno Karabakh, hinting that Azerbaijan may change its post-2020 war rhetoric, denying the existence of Nagorno Karabakh and claiming that the issue of status was thrown into the dustbin of history. There is a lack of details on what this autonomy could be. READ MORE
Peacekeeping in Karabakh Can Learn from the UNOMIG Experience  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
As Armenia and Azerbaijan come closer to launching bilateral negotiations over the normalisation of relations, many issues wait for a solution. Currently, the hottest debates are underway regarding the future status of Nagorno Karabakh and the legal modalities of the transit for Armenian and Azerbaijani goods passing each other territories. The war in Ukraine and the complete collapse of Russia – West relations added geopolitical components to the equilibrium. Do we have EU – Russia competition over the mediation process? Are there any disagreements between Brussels and Moscow on promoting lasting peace and stability in the South Caucasus? All these issues are worthy of being discussed and debated. READ MORE
Black Sea Security in Times of War 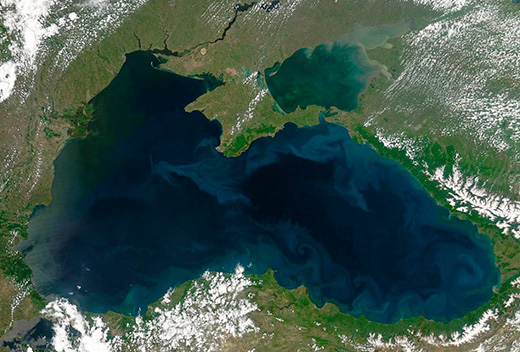 By Eugene KOGAN, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert By Eugene KOGAN, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert
There is no doubt that the ongoing Russian military action against Ukraine profoundly affects the rest of the Black Sea littoral states: Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania and Turkey. The tense standoff of recent weeks placed each of them in a difficult position between apprehension and, particularly with Turkey, a kind of peacemaker or rather mediator, which Russia now ignores completely.
Romanian Defence Minister, Vasile Dincu, said in January 2022 that “Russia, at the moment, is not a direct threat to Romania, but it is [rather] a threat to security in the [Black Sea] area”. The author disagrees with the minister’s statement since the Russian military, which is stationed on the occupied Crimean peninsula - not much more than 100 km from the Danube Delta – is a direct threat to Romania, even though Russian officials will blame the other side for posing a threat to Russia. Furthermore, the region’s three NATO member countries, namely Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey, have until today been unable to create and implement a comprehensive Black Sea security strategy together with NATO aspirants Georgia and Ukraine to counter the challenges posed by Russia. The latter, however, successfully implemented its divide and rule policy in the region. READ MORE.
A Path to a Peace Agreement between Armenia and Azerbaijan  By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin POGHOSYAN, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
While the world continues to follow the war in Ukraine and the growing tensions in relations between Russia and the West, Armenia and Azerbaijan are ready to launch negotiations to sign a peace treaty. All external powers involved in the region’s geopolitics – Russia, the US, the EU, Turkey, and Iran – support this process. Armenia and Azerbaijan will soon launch three separate, though interconnected, processes: the start of the work of the bilateral border delimitation and demarcation commission, the restoration of communications infrastructure, and the launch of negotiations on a peace treaty. These issues are discussed on two parallel platforms – Armenia-Azerbaijan-EU and Armenia-Azerbaijan-Russia. Both Russia and the EU support the start of work on all three tracks. READ MORE
Russia-China-Afghanistan  By Eugene KOGAN, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert By Eugene KOGAN, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert
Moscow and Beijing are likely to discover that their initial joy over the US withdrawal from Afghanistan may be premature. Afghanistan under the Taliban remains divided, insecure and uncertain about its current and future path. Without stability and security, neither Beijing nor Moscow will provide economic assistance while the international community will continue to shun Afghanistan.
Russia’s Presidential Envoy to Afghanistan, Zamir Kabulov, noted that “The Taliban were easier to negotiate with than the old “puppet government” of the exiled President Ashraf Ghani.” The latter was seen by, and from Moscow, as a puppet of the West and contacts that Russia maintained with Hamid Karzai’s successor were either downgraded or revised. At the same time, contacts between Russia and the Taliban only increased. With the West’s departure, Moscow is seizing up the opportunity indirectly to recognise the authority of the Taliban, which it officially designated as a terrorist organisation back in 2003 though without burning its bridges with the militant group. READ MORE.
Why non-aligned Azerbaijan signed an alliance declaration with Russia
 By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
On February 22, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev made an paid official trip visit to Moscow to discuss and sign a new declaration on allied cooperation with Russia. The visit came just a day after President Putin's infamous decision to recognize the independence of the so-called Donetsk People's Republic and Luhansk Peoples' Republic in Eastern Ukraine. President Vladimir Putin’s “unexpected” decision deteriorated relations with Ukraine, even more and was followed by the new round of economic sanctions imposed by the U.S and the EU.
President Aliyev's visit to Moscow triggered debates in Azerbaijan and Russia, respectively, on whether the main text of the declaration was pre-negotiated between the two leaders, or prepared amid the escalation around Ukraine. READ MORE
War and Peace in the South Caucasus: Putin Style  By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada
Without a doubt, Russia’s leader Vladimir Putin is the greatest factor in the risk of war between Russia and Ukraine. Yet paradoxically, Putin is perhaps the best hope for peace in the South Caucasus, at least as far as Azerbaijan and Armenia are concerned. The Georgian situation is, however, another matter. But one should take one step at a time in this exceptionally dangerous and conflict-prone region.
The recent 2020 Karabakh War between Azerbaijan and Armenia was, in effect, a continuation of the bitter 1990s ethno-religious territorial war over Nagorno-Karabakh (Artsakh) that emerged between the two newly independent states in the midst of the break-up of the Soviet Union. The 1990s conflict produced thousands of casualties and hundreds of thousands of displaced civilian ethnic minority refugees. It was a humanitarian catastrophe for families on both sides of the border. READ MORE
- February 28, 2022 20:03PM
Assessing the Urban Terrorism Strategy of the Kurdistan Workers' Party in Turkey
 By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad SHAHBAZOV, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
Since its emergence in the 1980s, the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) has been a significant source of concern to the state of Turkey. With the escalation of conflict between the Turkish state and the ethnic Kurdish community in the 1990s, the level of violence explicitly increased, and the civilian death toll rose to its highest point. Though the PKK could not ensure absolute authority in large, predominantly Kurdish provinces in the southeast, it gradually shifted to a new strategy —urban violence— to undermine the Turkish state's authority in Kurdish regions.
According to theories of violent resistance, violence is the only practical and productive tool of mass mobilisation of ethnic insurgencies against political systems. In the case of Kurdish nationalism in Turkey, many scholars argue that Turkey's policy of ethnic nationalism has had a decisive role in shaping Kurdish ethnic nationalism throughout these years. READ MORE
- February 28, 2022 19:44PM
Will Turkey Gamble with Ukraine against Russia?  By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly” By Yeghia TASHJIAN, Beirut-based regional analyst and researcher, columnist, "The Armenian Weekly”
In the past few years, Turkey has been gradually increasing its influence in Ukraine through trade and military cooperation amid escalating tensions between Moscow and Kyiv, challenging Moscow’s standing in the Black Sea region. The strategic cooperation between Ankara and Kyiv is not limited to political statements, but rather encompasses other important fields, such as the economy, security and defence industries. Moreover, relations between the two countries gained further impetus with Russia’s unification of Crimea in 2014 and reached their peak during the administration of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky, who assumed office in 2019. READ MORE
What's behind the Fresh Tensions between Iran and Azerbaijan?
 By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
In the period immediately after the 44-day Karabakh war, Baku-Tehran relations remained on the level of pragmatic co-operation, until the new conservative political establishment ascended to power in Iran. Since then, Tehran’s rhetoric against Azerbaijan has shifted from that of “partnership” to open threats that explicitly neglect the partnership atmosphere. Relations between Baku and Tehran have always been unstable, particularly at the beginning of the 2000s. However, they rekindled when both countries became engaged in regional infrastructure and transit projects. READ MORE
- December 15, 2021 09:08AM
Delimitation, Demarcation and Cartographic Manipulation in the Wake of the 44 Days War  By Hayk KOTANJIAN, Lieutenant General (Ret.), D.Sc., Professor of Political Science of the RA, RF, USA (state studies-strategic security studies), Full Member of the Academy of Military Sciences of the RF By Hayk KOTANJIAN, Lieutenant General (Ret.), D.Sc., Professor of Political Science of the RA, RF, USA (state studies-strategic security studies), Full Member of the Academy of Military Sciences of the RF
In the wake of the 44-day war in 2020, an unprecedented escalation of the process of delimitation and demarcation of the Armenian-Azerbaijani borders has been launched. This was done contrary to the principles and procedure for border delimitation and demarcation recommended by the OSCE Secretariat. The unparalleled pressure on the Armenian population from Karabakh was accompanied by subsequent attempts to undermine the settlement process under the auspices of the OSCE Minsk Group co-chairmanship. Among the arguments substantiating claims to include Nagorno-Karabakh in Azerbaijan, Baku authorities refer to the Azerbaijani-language toponymy, which allegedly has a long history. READ MORE
Armenia's Options in the Face of Coercive Azerbaijani Tactics Are Limited  By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
The developments of the last year proved that assessments according to which by taking some 8500 square km of territories in the 2020 Karabakh war, Azerbaijan will be satisfied and an era of peaceful development will be launched for Armenians, were highly exaggerated, and had little semblance to reality.
Since the end of the 2020 Karabakh war, Armenia has faced a new, harsh reality along its borders with Azerbaijan. Some in Armenia hoped that after taking back most of the territories which Baku lost during the first Karabakh war of 1992-1994, an era of regional peace would start in the South Caucasus, while Azerbaijan would agree to continue negotiations to fix the status of Nagorno Karabakh within its 1988 borders. Baku was quite quick to dampen such perceptions. Azerbaijan established an economic region of Karabakh in July 2021 and started to aggressively push forward the narrative that war had ended not only the conflict, but Nagorno Karabakh itself, and thus it was senseless to negotiate over the status of a non-existing entity. READ MORE
Azerbaijan-Armenia Border Dispute – Could the Conflict Re-escalate?  By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst By Fuad Shahbazov, Baku-based independent regional security and defence analyst
Half a year after the Russian-brokered ceasefire agreement was signed between Azerbaijan and Armenia ending the 44-day war in Karabakh, peace in the complex region is not on the horizon. A new stage of discontent and harsh statements came last week after Azerbaijani Armed Forces reportedly crossed the border with Armenia in the Syunik province and advanced around 3 kilometres by Sev Lake. Yerevan dubbed this action as an explicit provocation and an attempt to occupy Armenian territory, whereas Baku denied the accusations, stating that Azerbaijani border guards established a military control point at the heights around the lake without advancing into Armenian territories. READ MORE
- September 14, 2021 19:40PM
Polish-Romanian Defence and Security Policy  By Eugene Kogan, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert By Eugene Kogan, Tbilisi-based defence and security expert
A joint initiative of Romanian President Klaus Iohannis and Polish President Andrzej Duda, known as the ‘Bucharest Nine', was launched in November 2015 and laid a foundation for foreign and security policy meetings and discussions. As the next step, the Warsaw NATO Summit in July 2016 accelerated military-to-military cooperation. As a result, the initiative brought Romanian troops to Poland and Polish troops to Romania on a rotational basis in March 2017. In addition, their pivotal positions in the east and in the south of NATO’s reach have further increased their cooperation in a variety of defence and security programmes. READ MORE.
The Karabakh War: The Lessons of Defeat in the Cyberspace  By Lieutenant-General (Ret.) Hayk S. Kotanjian, PhD, Professor Strategic Security Studies By Lieutenant-General (Ret.) Hayk S. Kotanjian, PhD, Professor Strategic Security Studies
Reflecting on the lessons of the military aggression of Turkey and Azerbaijan against the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic and the Republic of Armenia, strategic analysts of the security institutions and processes continue to monitor the dynamics of the peace-war around Karabakh in the context of the world order transformation. Russian President Vladimir Putin at the session of the Russian Security Council of March 26, 2021, emphasizing the exceptional role of cybersecurity, pointed out the strategic priority of the development of the cyberspace resources management system. In general, this coincides with the assessments of the special significance of this security sector, voiced recently by the US President Joe Biden and Chinese President Xi Jinping. READ MORE
Armenia’s Endgame in the Aftermath of the 2020 Karabakh War Needs to be Clarified  By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
Still recovering from the war, it is not yet clear what Armenia's strategy is for Nagorno Karabakh. Without a coherent and consistent policy from the Armenian government, Armenia may lose what it retains of the enclave.
Almost four and half months after the end of the 2020 Karabakh war, Armenia has not yet recovered. Society is grappling with lingering questions about the reasons for the staggering defeat. The fate of the remaining Armenian prisoners of war in Azerbaijan, whose POW status Azerbaijan refuses to accept, is a top priority. The ongoing de facto border demarcation process in the Syunik region, and looming demarcations in other regions, have put additional stress on society. The current political crisis and upcoming June 20, 2021, snap parliamentary elections do not help restore stability. Different political forces actively discuss possible changes in the electoral code, and even the possibility of making some amendments to the Constitution before the elections. However, apart from the daily ups and downs of politics, Armenia faces a bigger task: that of clarifying its stance on fundamental issues regarding the new status quo in Nagorno-Karabakh. READ MORE
Potential Stress Points in the Nagorno-Karabakh Ceasefire Agreement  By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada
There are number of potential stress points in the ceasefire agreement signed by Russia, Azerbaijan and Armenia, but also agreed to by the president of Nagorno Karabakh on November 9th, 2020. It is a document that was signed under the duress of rapidly deteriorating war conditions for Armenians. Few within Armenia were consulted apart from some senior military leaders. It has not been ratified by the Armenian Parliament. Public disapproval has been extensive READ MORE.
In 2021 Armenia Can Only Wait and Watch whilst Others Decide the Fate of Karabakh  By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies By Benyamin Poghosyan, PhD, Chairman, Center for Political and Economic Strategic Studies
Since the end of the second Karabakh war in November 2020, Armenian, Azerbaijani, and international pundits have published many opinions and assessments focusing on the war, its causes and consequences, and the decisive victory of Azerbaijan. The strategic blunders of the Pashinyan government, the Russia – Turkey deal, and the aloofness of the US, are among the hotly debated issues about what contributed to the launch of the war, and the capitulation of Armenia. Some experts seek to forecast the distant future (5-10 years). They argue that Armenia will accept its defeat, will forget about territories taken by Azerbaijan during the war, and will seek to get material benefits through establishing economic cooperation with Baku and Ankara. READ MORE
- February 25, 2021 07:32AM
How to Break the Current Deadlock in Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict Resolution: Strategic Dialogue on the Peace Process within a Boosted Peace Context?
2020 Research Digest, edited by George Vlad NICULESCU, EGF Head of Research
The 2020 European Geopolitical Forum Research Digest aimed to explore the resilience of the Nagorno-Karabakh (NK) peace process driven by the implementation of the Madrid/Basic Principles, and the increased relevance of the peace context, created by various initiatives aiming to incentivize peaceful conflict resolution. It consists of three research papers drafted by distinguished Armenian, Azerbaijani, and Russian experts, who have been invited to respond generic questions such as: Are the Madrid Principles really dead? Why haven’t they been implemented so far? What are the Armenian perceived downsides of the Madrid Principles as the most plausible option for the Karabakh conflict resolution? Why does Azerbaijan support the Madrid Principles, and why does Baku believe they could still lead the way to a breakthrough in the peace process? What structural, institutional, conceptual, or operational changes could unblock the NK peace process, while taking advantage from a much needed boost of the peace context? READ MORE
Expert Peer-Review
 By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada
By Alan Whitehorn, Professor Emeritus in Political Science, The Royal Military College of Canada
When there is so much shelling and yelling in the South Caucasus conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, it is helpful to read a collection of thoughtful essays by knowledgeable authors from several differing countries and perspectives that appeared in The European Geopolitical Forum. Each piece is a welcome contribution, but nevertheless has key gaps and issues. I will comment on each in the order in which they appear. READ THE REVIEW
Nagorno-Karabakh Crisis: Azerbaijan’s Fraying Temper  By Khayal Iskandarov Ibrahim, Rashad Tahirov Kamal, PhD in philology, associate professor Sadi Sadiyev Saleh By Khayal Iskandarov Ibrahim, Rashad Tahirov Kamal, PhD in philology, associate professor Sadi Sadiyev Saleh
Another escalation in Nagorno-Karabakh in early morning on September 27, 2020 brought Armenian-Azerbaijani conflict once again to the focus of world community. Approximately 30 years have elapsed since this conflict was initiated. However, there has not been any substantial progress in the efforts to solve the problem. The prominent political figures in Armenia, who more or less understood the consequences of their actions and endeavored to solve the problem, were either ousted or assassinated. READ MORE.
|
|